Systemic inflammation, gut health and collagen

Collagen and its role in systemic inflammation: What is systemic inflammation and how does it affect health?
Systemic inflammation is a type of inflammation that affects the entire body, not just a specific area or organ. It is part of the body’s immune system and can occur in response to infection, injury, or prolonged exposure to various risk factors. However, when inflammation becomes chronic and is no longer a temporary response to a harmful stimulus, it can lead to serious health problems. Collagen, a structural protein found throughout the body, has been shown to play an important role in managing systemic inflammation and its negative effects on health. This article will explore what systemic inflammation is, its causes, and how collagen can play a crucial role in reducing its effects and supporting the body during inflammatory processes.
What is systemic inflammation?
Systemic inflammation is a general form of inflammation that spreads throughout the body, as opposed to localized inflammation that only affects a specific area, such as an injury or infection. Inflammation is the body's natural response to infection, injury, or harmful substances, and it has an important function in protecting the body and promoting healing. However, when inflammation becomes chronic, it can cause problems and lead to a number of health conditions.
Systemic inflammation is characterized by an increase in inflammatory markers in the blood, such as C-reactive protein (CRP), and an activation of the immune system that can affect multiple organs and tissues in the body. This can lead to a wide range of negative effects, as chronic inflammation is linked to many diseases, including cardiovascular disease, diabetes, cancer, and autoimmune diseases.
Causes of systemic inflammation
There are several factors that can contribute to the onset of systemic inflammation. Some of the most common causes include:
1. Chronic diseases
Diseases such as type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, arthritis, and certain types of cancer can cause chronic inflammation in the body. These diseases make it difficult for the body to regulate inflammation and can create a long-term inflammatory process.
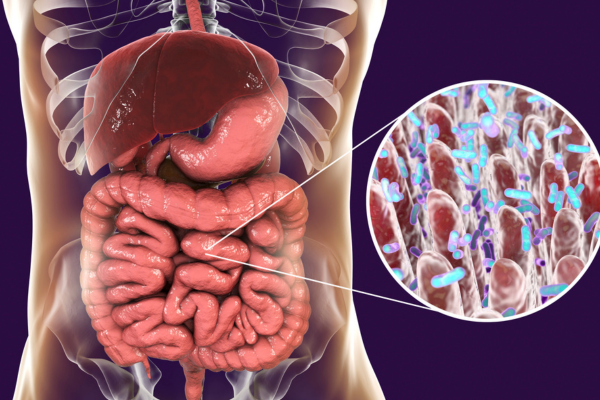
2. Imbalance in the intestinal flora (dysbiosis)
The gut contains trillions of microbes that are crucial to health and immune function. When the balance of gut flora is disrupted, known as dysbiosis, it can lead to increased permeability in the gut, allowing bacteria and toxins to leak into the bloodstream. This triggers the body's immune system and can lead to systemic inflammation.
3. Lifestyle factors
Poor diet, smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, lack of physical activity and high stress can all contribute to increased inflammation in the body. A diet high in processed foods and sugar is particularly known to drive inflammatory processes.
4. Environmental toxins
Exposure to environmental pollutants, chemicals, and heavy metals can also cause inflammation in the body. These toxins can trigger the immune system and cause chronic low-grade inflammation.
5. Autoimmune diseases
In autoimmune diseases, the immune system attacks the body's own tissues, leading to inflammation. Diseases such as lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, and Crohn's disease are examples of diseases where systemic inflammation is a hallmark.
What health problems can systemic inflammation cause?
Chronic systemic inflammation can have serious long-term effects on health. When inflammation is not properly regulated, it can give rise to several diseases and conditions, including:
1. Cardiovascular diseases
Long-term inflammation plays a major role in the development of atherosclerosis, a disease in which plaque builds up in the arteries, which can lead to heart attacks, strokes, and other cardiovascular diseases.
2. Diabetes
Systemic inflammation is linked to insulin resistance, a condition in which the body's cells do not respond effectively to insulin. This is one of the primary causes of type 2 diabetes.
3. Arthritis and joint problems
Inflammation is a central cause of pain and swelling in joint inflammation, such as rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. In these diseases, inflammation leads to the breakdown of cartilage and joint tissue.
4. Autoimmune diseases
Systemic inflammation is also a hallmark of autoimmune diseases where the immune system attacks the body's own tissues, leading to tissue damage and functional impairment. For example, lupus, MS, and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
5. Cancer
Chronic inflammation can contribute to the development of cancer. Inflammation can affect the genetic material of cells and create an environment in which cancer can grow and spread.
6. Neurodegenerative diseases
Diseases such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease have been linked to increased inflammation in the brain. Prolonged inflammation can affect brain function and contribute to neurodegeneration.
7. Skin problems
Systemic inflammation can affect skin health and contribute to diseases such as eczema, psoriasis, and rosacea.
Collagen and its role in systemic inflammation
Collagen is the body's most abundant protein and plays a central role in providing structure and strength to skin, bones, tendons, joints and blood vessels. Collagen acts as a kind of "glue" to hold tissues together and ensure they function properly. Collagen is also important for healing and repairing tissues, making it especially relevant when the body is exposed to injury or inflammation.
When it comes to systemic inflammation, collagen may have several important functions:
1. Supports tissue repair and healing
Collagen is a key component in the healing process after injury and inflammation. In the event of inflammation and tissue damage, collagen plays a role in building the tissue needed to repair the damaged areas. By ensuring healthy collagen production, the body can recover more quickly from damage caused by systemic inflammation.
2. Reduced degradation of cartilage and joints
In arthritis and joint inflammation, which are often caused by systemic inflammation, collagen is an important part of the structure of cartilage. Collagen acts as a cushioning structure that helps maintain joint function and flexibility. In chronic inflammation, collagen breaks down faster, leading to impaired joint function. By taking collagen supplements, you can support cartilage health and slow down the breakdown.
3. Improves skin elasticity and strength
Collagen plays a crucial role in maintaining skin firmness and elasticity. In systemic inflammation, the skin can be affected, and collagen production can decrease. By supporting collagen production, you can improve skin structure and counteract the effects of aging, while helping the skin heal from inflammation and damage.
4. Strengthens blood vessels and blood flow
Collagen is found in the walls of blood vessels and helps keep them strong and elastic. In systemic inflammation, blood vessels can become more prone to damage and become more permeable. Collagen can help maintain the integrity of blood vessels and counteract the harmful effects of inflammation on circulation.
5. Immune system regulation
Research suggests that collagen may help regulate the immune system's response to inflammation. By supporting tissue repair and reducing inflammatory processes, collagen may help reduce the overactive inflammation that characterizes many autoimmune diseases.
How can collagen intake help reduce systemic inflammation?
Research has shown that collagen intake may be beneficial in reducing the effects of systemic inflammation. Collagen can be taken as a supplement in powder, capsule, or liquid form, and has been shown to support collagen production in the body, promote joint health, improve skin texture, and reduce inflammation.
1. Collagen as an anti-inflammatory agent
Collagen can help modulate the immune system and reduce inflammatory processes. Because collagen contains amino acids like glycine and proline, which are important for rebuilding tissues, it can help reduce inflammation in joints and skin and support recovery from injuries.
2. Joints and muscles
For people suffering from joint inflammation and pain related to systemic inflammation, collagen can provide support to relieve pain and improve joint mobility by strengthening the cartilage and muscles around the joints.
Conclusion
Systemic inflammation is a serious health problem that can contribute to the development of many chronic diseases and conditions. Collagen, which plays a critical role in the structural functions of the body, has been shown to be effective in supporting tissue healing, reducing inflammation, and improving health in cases of systemic inflammation. By optimizing collagen production and using collagen supplements, people with systemic inflammation can take advantage of the benefits that collagen provides to promote healing, reduce inflammation, and support overall health.